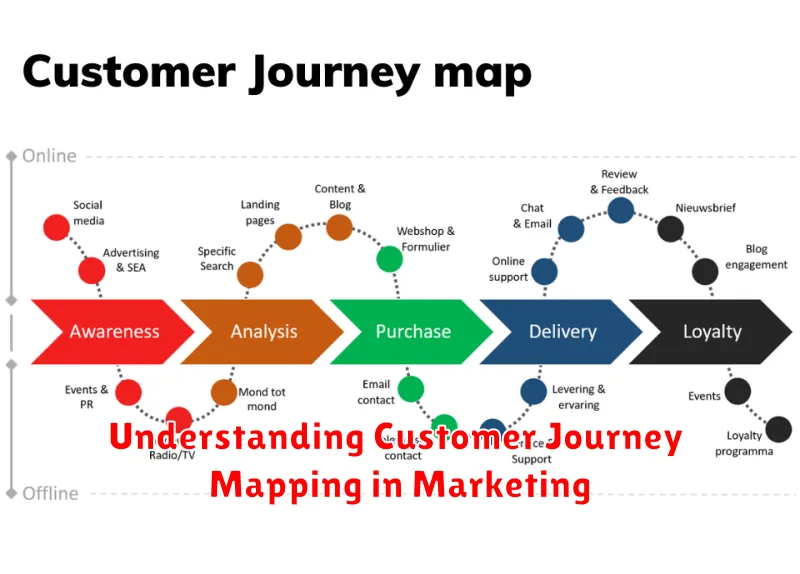
In today’s competitive market, understanding the customer journey is paramount to marketing success. Customer journey mapping is a powerful technique that allows businesses to visualize the steps their customers take, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement. By meticulously charting this customer journey, marketers gain invaluable insights into customer behavior, motivations, pain points, and touchpoints. This understanding enables them to optimize marketing strategies, improve customer experience, and ultimately drive conversions and loyalty. This article delves into the essentials of customer journey mapping in marketing, providing a comprehensive overview of its benefits, components, and practical application.
Customer journey mapping goes beyond simply identifying the steps a customer takes; it provides a deep dive into the emotions, thoughts, and actions that characterize each stage. By adopting a customer-centric approach and leveraging customer journey mapping, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and expectations of their target audience at every point in their journey. This strategic approach not only enhances the overall customer experience but also fosters stronger, more meaningful customer relationships. Through this exploration of customer journey mapping, you will gain the knowledge and tools necessary to create effective maps that empower you to connect with your customers on a deeper level and drive business growth.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the process a customer goes through in engaging with a company, product, or service. It outlines all the touchpoints a customer encounters, from initial awareness to post-purchase experience and beyond.
The map illustrates the customer’s actions, thoughts, and emotions at each stage of their interaction. This provides businesses with valuable insights into the customer experience, enabling them to identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and areas to enhance customer satisfaction.
Essentially, a customer journey map helps businesses understand the customer’s perspective and provides a framework for optimizing the customer experience across all channels and touchpoints.
Stages of the Customer Journey
The customer journey is typically divided into key stages, each representing a different interaction point between the customer and a brand. Understanding these stages is crucial for effective marketing.
Generally, the customer journey includes the following core stages:
- Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem and begins researching potential solutions. This is where brand visibility and initial impressions are critical.
- Consideration: The customer evaluates different options, comparing features, benefits, and prices. Providing compelling information and addressing customer concerns is key at this stage.
- Decision/Purchase: The customer chooses a solution and makes a purchase. A seamless and positive purchase experience is essential.
- Retention/Advocacy: Post-purchase, the focus shifts to customer satisfaction and building loyalty. Excellent customer service, follow-up communication, and loyalty programs can foster advocacy.
While these stages provide a general framework, the specific steps and touchpoints within each stage can vary depending on the industry, product, and target audience.
Collecting Data to Inform the Map
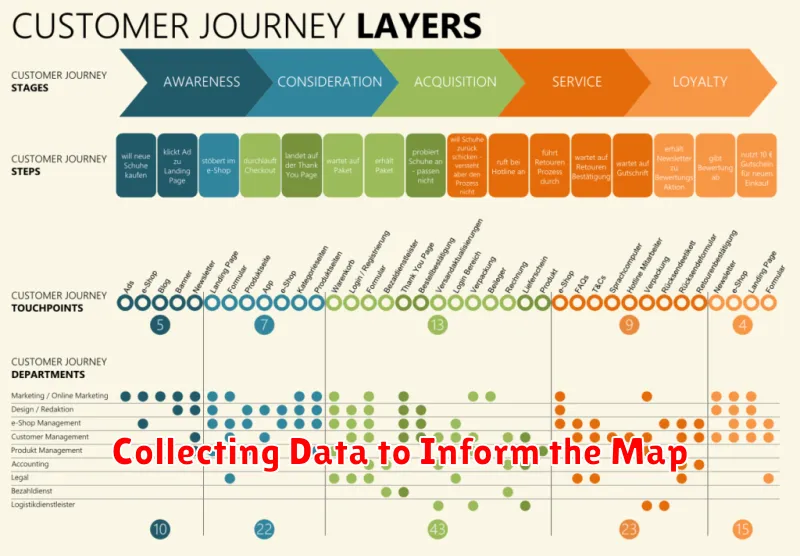
Gathering accurate data is crucial for creating a useful customer journey map. This data should represent the actual customer experience, not assumptions or internal perspectives. Multiple data sources provide a more holistic view.
Key Data Sources
Analytics Data: Website analytics, marketing automation platforms, and CRM systems offer quantitative insights into customer behavior. This data reveals how customers interact with your website, marketing campaigns, and sales team.
Qualitative Research: Customer interviews, surveys, and focus groups provide valuable context and emotional insights that quantitative data often misses. Directly asking customers about their experiences offers a deeper understanding of their needs, motivations, and pain points.
Operational Data: Internal data from sales, customer service, and other departments can highlight operational inefficiencies or bottlenecks affecting the customer journey. Reviewing support tickets, call logs, and sales data can uncover areas for improvement.
Visualizing the Journey
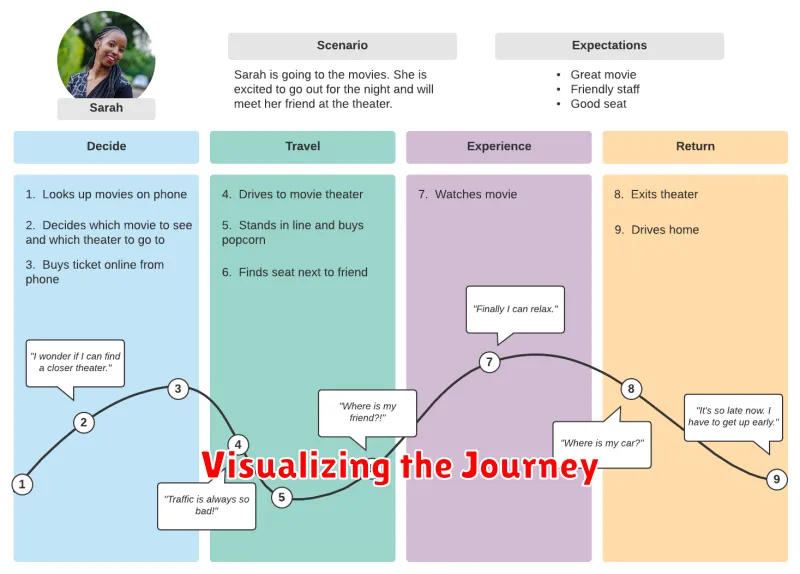
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the process a customer goes through in engaging with your brand. It illustrates all the touchpoints a customer has with your business, from initial awareness to post-purchase interaction. Visualizing this journey helps marketers understand the customer experience from the customer’s perspective.
Common visualization methods include using a timeline format, which shows the steps in chronological order. Other approaches include using a circular diagram to highlight the cyclical nature of customer engagement or a swimlane diagram to show the interaction between the customer and different departments within the company.
Regardless of the specific visualization chosen, the key is to clearly and concisely present the key stages of the customer journey, the customer’s actions, thoughts, and emotions at each stage, and the touchpoints they interact with. This visual representation allows stakeholders to easily identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and moments to enhance the customer experience.
Identifying Friction Points
A crucial aspect of customer journey mapping is identifying friction points. These are any points in the journey where the customer experiences difficulty, frustration, or hesitation.
Friction points can manifest in various forms. For example, a complicated checkout process, unclear website navigation, or unhelpful customer service interactions can all create friction.
Identifying these pain points requires careful analysis of each stage of the customer journey. Look for areas where customers abandon their carts, submit negative feedback, or require repeated assistance.
Analyzing available data, such as website analytics, customer service logs, and survey results, can provide valuable insights into these areas of friction.
Using the Map to Improve Conversions
A customer journey map, once created, isn’t simply a static document. It serves as a dynamic tool for optimizing the customer experience and, ultimately, driving conversions. By analyzing each touchpoint, marketers can identify areas of friction or opportunities for enhancement.
Identifying Pain Points: The map highlights areas where customers experience frustration or drop off. These pain points might include a confusing website navigation, a complex checkout process, or unhelpful customer service interactions.
Optimizing Touchpoints: By addressing these pain points, businesses can streamline the customer journey. This might involve simplifying forms, providing clearer instructions, or offering more personalized support.
Personalization and Targeting: Understanding the customer’s mindset at each stage allows for more effective targeting and personalized messaging. This can lead to increased engagement and higher conversion rates.
Updating the Map as Customer Behavior Evolves
Customer journey maps are not static documents. Customer behavior constantly evolves due to various factors, including technological advancements, economic shifts, and changing social trends. Therefore, it’s crucial to regularly update your customer journey map to ensure it accurately reflects the current customer experience.
The frequency of updates depends on the dynamics of your industry and the speed of change in your target market. Some businesses might require updates every few months, while others can review their maps annually. Regardless of the frequency, a systematic approach to updating is essential.
Reviewing website analytics, customer feedback surveys, and sales data can provide valuable insights into evolving customer behavior. Analyzing these data points can highlight new touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. Incorporate these findings into the updated map to maintain its relevance and effectiveness.